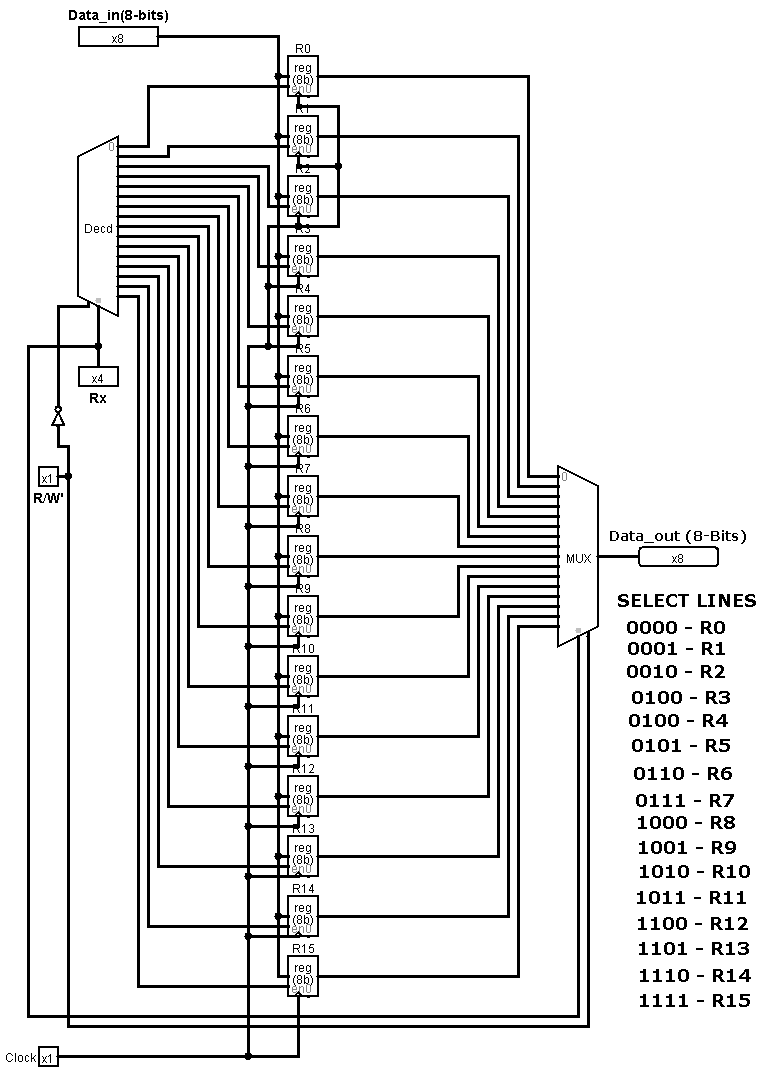
A register file is a small, high-speed memory component within the Central Processing Unit (CPU) that stores temporary data, known as registers, which are used during the execution of instructions. Registers are essential for fast data processing, providing the CPU with immediate access to frequently used values like operands and intermediate results. Unlike non-volatile memory, registers are volatile, meaning their contents are lost when power is turned off. The register file is typically made up of a limited number of registers, which vary depending on the architecture of the processor, and is designed to allow the CPU to access and modify data with minimal delay, often in a single clock cycle.
Key Characteristics: